Fertility naturally declines with age – most women are most fertile in their 20s, with chances of conception gradually dropping in the 30s and declining more sharply after 35. Understanding fertility vs age is crucial for women planning pregnancies, and SensIQ provides science-backed insights to guide reproductive decisions.
SensIQ, a neurologist-formulated system, offers personalized plans to address brain and mood changes during this phase while also guiding women through perimenopause and menopause.
This perspective helps women considering fertility preservation or planning future pregnancies make informed choices.
Key Takeaways
- Fertility begins to decline gradually after age 30, with a more significant drop after 35, impacting both egg quality and conception chances.
- Women are born with all the eggs they will ever have, and by age 40, approximately 90% of those eggs are gone, affecting fertility.
- The best time for pregnancy is in the late 20s to early 30s, as fertility is optimal during this period, making it the ideal age for women to conceive.
- Male fertility also declines with age, particularly after 40, with decreased sperm quality affecting conception chances and increasing the risk of complications.
- Fertility treatments like IVF and egg freezing can assist women over 35 in overcoming age-related fertility challenges, but success rates decrease as age increases.
How Age Affects Female Fertility
Peak Fertility Age: When Are You Most Fertile?
Fertility is at its peak in a woman’s childbearing age, typically in her 20s and early 30s. During this time, egg quality is high, and the chances of a successful pregnancy are greatest. However, after age 30, fertility starts to decline gradually, with the decline becoming more significant after the age of 35. At this point, the chances of falling pregnant at 35 begin to decrease, and this decline becomes even more pronounced as women enter their 40s.
Egg Quality by Age: Impact on Conception
As women age, the quality of their eggs begins to deteriorate. This decline in egg quality starts around age 30 and accelerates after 35. The female fertility age chart illustrates how fertility declines with age. Women are born with all the eggs they will ever have, and over time, the number and quality of those eggs decrease, making it harder to conceive naturally.
Women in their childbearing age may start to notice subtle changes in menstrual cycles and hormone patterns, which can influence fertility and conception.
At What Age Are 90% of Your Eggs Gone?
By the time a woman reaches her early 40s, approximately 90% of her eggs are gone. This natural decline impacts fertility and the chances of getting pregnant without the assistance of fertility treatments. This change is illustrated by the female fertility graph, which shows the stark contrast in fertility rates between women in their 20s and those in their 40s.
What Happens to Fertility at 35 and 40? A Breakdown
At age 35, fertility begins to decline more rapidly. By age 40, the number of eggs left decreases significantly, and the fertility chart by age highlights a sharp drop in fertility levels.
Women over 40 face increased challenges in conception, and the risk of miscarriage also rises significantly. These changes are crucial when considering family planning, as the average age for first-time mothers is now creeping up, but fertility becomes more difficult after 35.
Women classified under advanced maternal age may face increased risks related to egg quality, chromosomal abnormalities, and fertility treatments, making early awareness essential.
Fertility Decline and Age: What Women Need to Know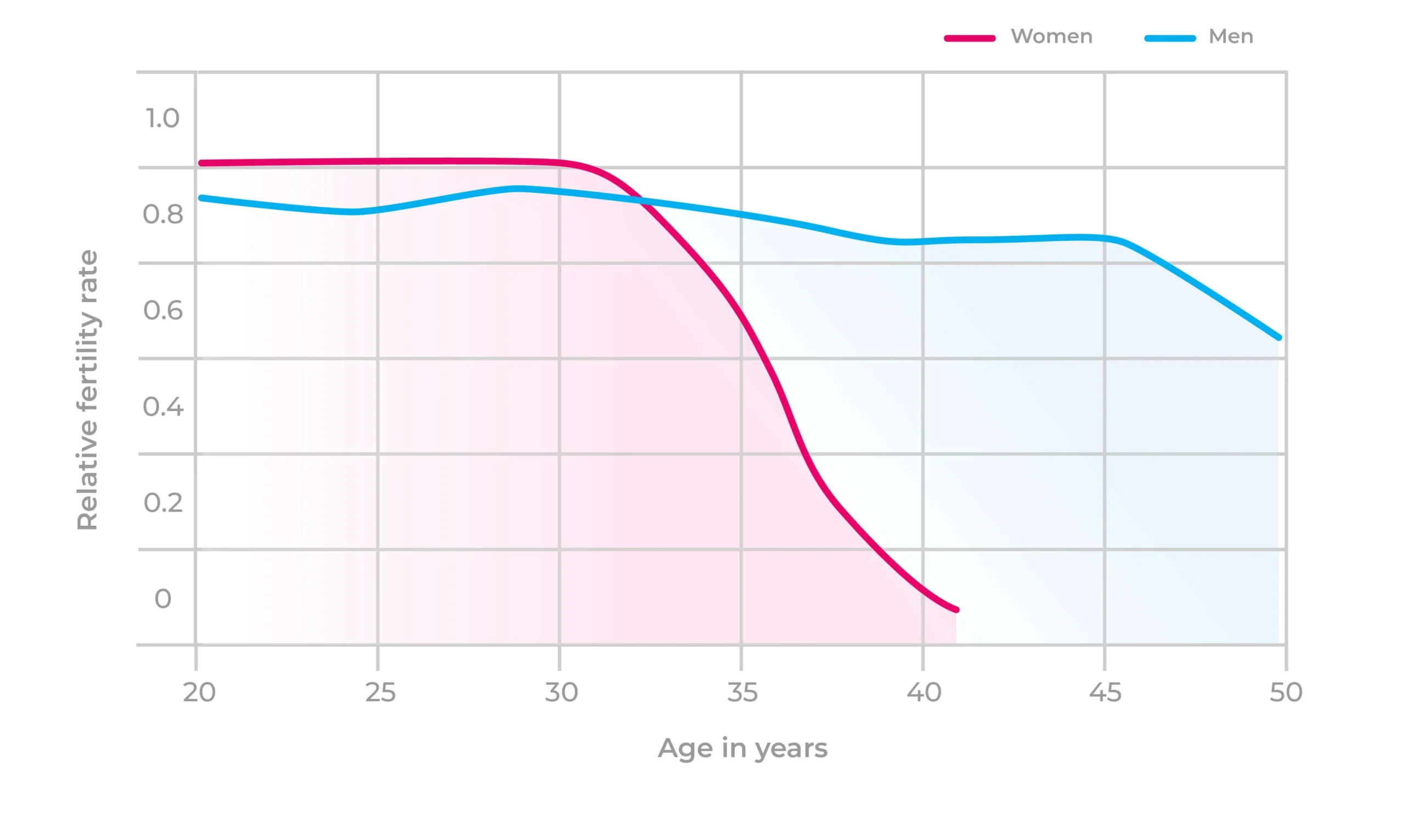 Pregnancy Age Limit: When Is It Too Late to Have Children?
Pregnancy Age Limit: When Is It Too Late to Have Children?
Although fertility declines with age, many women can still conceive into their 40s with medical help. However, after age 45, conception becomes more difficult, and the advanced maternal age category comes into play, which is associated with a higher risk of complications such as gestational diabetes and high blood pressure. It’s important to consider this decline when planning a pregnancy, as the chances of falling pregnant naturally significantly decrease after this age.
Female Fertility Age 50: Can You Still Conceive?
It is biologically possible for women to conceive at age 50 with fertility treatments such as egg freezing or in vitro fertilization (IVF). However, the success rates for these procedures drop significantly at this stage, and the risk of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities increases. At this age, fertility specialists often recommend assisted reproductive technologies to help achieve a live birth, but the chances are lower compared to women in their 30s.
Does Age Really Affect Fertility? The Truth About Declining Fertility
Yes, age has a significant impact on fertility. As women age, the number of eggs decreases, and the quality of remaining eggs diminishes. The female fertility age chart and female fertility graph clearly demonstrate this decline, showing that fertility starts to decline earlier for women than for men. By age 35, the chances of falling pregnant at 35 are lower, and by 40, the fertility decline is much more significant.
Best Age for Pregnancy for Females: When to Start Thinking About Fertility
The best age for pregnancy for females is typically in the late 20s to early 30s, when fertility is at its peak. Women who wait until their mid-30s or later may face more challenges, as egg quality and the number of viable eggs decline. If you are planning to delay pregnancy, it’s essential to understand the important factors involved, such as egg quality, and consider fertility preservation options like egg freezing.
Male Fertility and Age: What Men Should Know
Men’s Fertility Age: How Aging Affects Male Reproductive Health
Unlike women, men produce sperm throughout their lives. However, as men age, sperm quality and quantity decline. This decrease begins around age 40, and the fertility success rates for men over 40 are lower than for younger men. Additionally, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in sperm increases as men age, which can affect the chances of a healthy pregnancy.
Male Fertility Age 40: Impact on Conception
At age 40 and older, men may experience a decline in sperm motility and genetic quality, which can reduce the likelihood of successful conception. However, it is still possible for men to father children later in life, though the chances of pregnancy are lower. As with women, the increased risk of complications and birth defects can arise due to reduced sperm quality.
Male and Female Fertility Age Graph: A Comparative View
A fertility age graph compares male and female fertility over time. While female fertility drops sharply after 30, male fertility gradually declines after age 40. This comparison helps highlight the different timelines for fertility between the sexes, with men having a longer period to father children without the same fertility challenges women face.
What Happens to Male Fertility After 40? Key Insights
After 40, men may experience decreased sperm quality and motility, leading to challenges in conception. While men can still father children later in life, the risk of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities increases with age, which is why seeking fertility treatments is recommended if conception proves difficult.
Preserving Fertility: Options and Timing

Fertility Age Graph: Understanding Your Reproductive Options
The fertility age graph helps women understand when their fertility begins to decline and when it might be time to consider fertility preservation methods such as egg freezing. The graph clearly shows that fertility starts to decline around 30 and continues to decrease, becoming much more noticeable by age 35.
Fertility Testing and Preservation Options for Women
Fertility testing is a critical first step for women who want to understand their reproductive health. Tests can evaluate egg reserve and egg quality, which helps women decide if they need to pursue options like egg freezing or IVF for future pregnancies. For women interested in delaying childbearing, egg freezing is an option to preserve fertility at a younger age.
When Should You Start Thinking About Egg Freezing?
The best time to consider egg freezing is in your early 30s, when egg quality is still relatively high. This option provides flexibility for women who wish to delay childbearing but want to maintain their chances of a healthy pregnancy later on.
Fertility Treatment Options: When to Seek Help
Fertility Treatments for Women: Navigating Your Options After 35
Women over 35 who are struggling with fertility may need to explore options like IVF, egg freezing, or IUI. These fertility treatments can help overcome age-related fertility challenges by assisting with egg retrieval, sperm selection, and embryo implantation.
Fertility by Age Chart: Understanding Treatment Options Over Time
A fertility by age chart provides a visual representation of when certain fertility treatments are most effective based on a woman’s age. For women in their 30s and early 40s, treatments like IVF with egg retrieval have the highest success rates for a live birth.
At what age are you most fertile?
Women are most fertile in their 20s and early 30s when egg quality is at its highest.
At what age does fertility begin to decline for women?
Fertility starts to decline gradually after age 30, with a more significant decline after 35.
What happens to male fertility after 40?
Men experience a decline in sperm quality and motility after age 40, affecting conception chances.
What is the best age to get pregnant?
The best age to get pregnant is in the late 20s to early 30s, when fertility is optimal.
When is it too late to have children?
It becomes increasingly difficult to conceive naturally after age 40, though fertility treatments can still help.
How does egg quality affect fertility at different ages?
Egg quality decreases as women age, especially after 35, making it harder to conceive naturally.


