Flu brain fog refers to changes in thinking and focus that can occur during or after the flu. These changes may include slower thinking, poor attention, or mental tiredness.
Flu brain fog does not mean brain damage. It reflects how the body’s immune response affects brain function during illness. In most cases, symptoms improve as the body recovers.
Researchers continue to explore can the flu cause brain fog as part of the body’s immune response during viral illness.
Key Takeaways
- Flu brain fog refers to temporary changes in focus, memory, and mental clarity that can occur during or after influenza and are linked to the body’s immune response, not brain damage.
- Inflammation and immune signaling can affect how brain cells communicate, potentially slowing cognition and attention while the body prioritizes recovery.
- Symptoms often improve gradually; however, brain fog after the flu can persist longer in some individuals, depending on sleep, stress, and overall health.
- Supportive care,e such as rest, hydration, and reduced mental strain, helps recovery by allowing normal brain function to return over time.
- Persistent or worsening cognitive symptoms should be evaluated by a clinician to rule out complications or overlapping conditions.
What Flu Brain Fog Feels Like
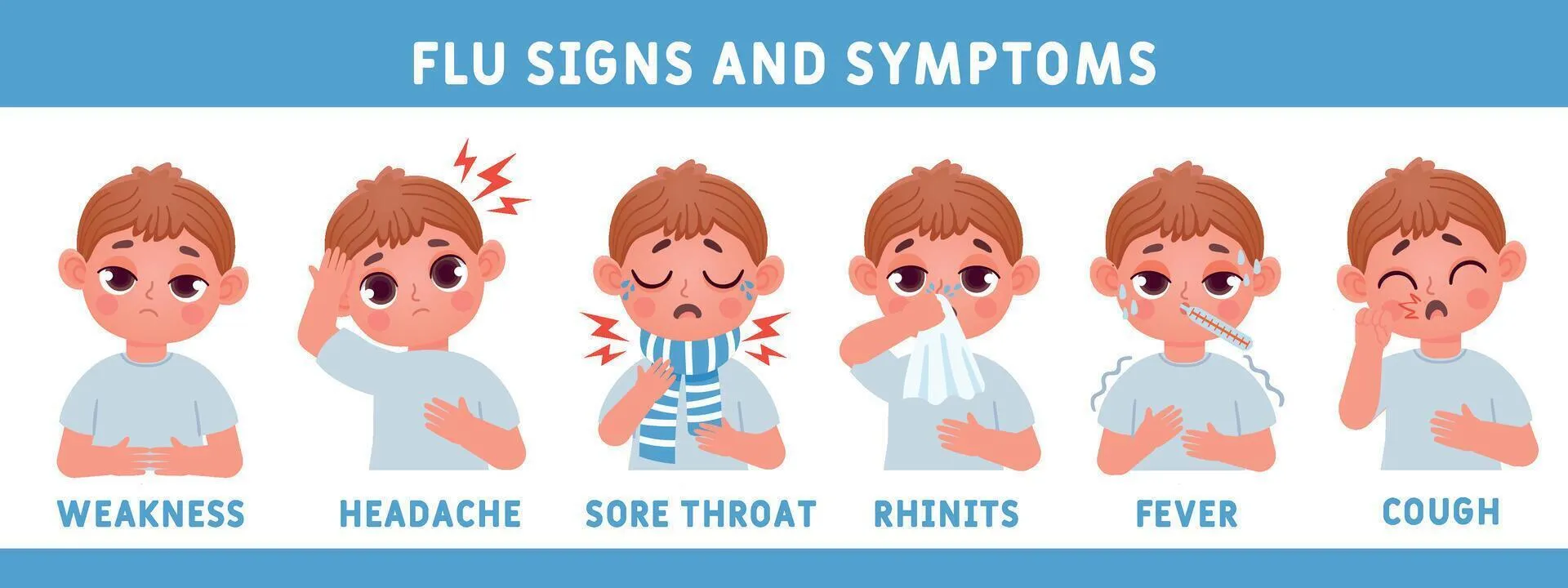
Common flu brain symptoms
Common symptoms include poor focus, slower thinking, and forgetfulness. Some individuals experience mental “foggy” or reduced alertness. These cognitive symptoms often appear with fatigue. Their intensity varies from person to person.
Tasks that normally feel easy may require more effort. Work, school, or planning can feel harder. These changes reflect temporary strain, not loss of ability.
Brain fog when sick with a cold or flu
Brain fog can occur with other viral illnesses, including the common cold. Fever, poor sleep, and low energy can worsen mental clarity. The experience may feel similar across infections. Recovery patterns often overlap.
Flu Brain Fog After Illness
During an active flu infection
During the flu, brain fog often appears alongside fever and body aches. Mental clarity may drop as symptoms peak. The brain focuses on supporting the body’s immune response. This shift can reduce attention and processing speed.
After flu recovery
For some individuals, brain fog after the flu persists even after physical symptoms have improved. Fatigue, poor sleep, or stress may slow recovery. This uneven pattern can feel confusing. It does not indicate damage.
Many people report brain fog after the flu that lingers even after other symptoms have improved.
How Long Does Flu Brain Fog Last?
Typical recovery timelines
Most people notice gradual improvement over days or weeks. Mental clarity often returns as energy levels improve. Short-term symptoms are common. Longer recovery does not mean harm.
Why duration vary between people
Recovery time depends on sleep, stress, and overall health. Strong immune responses may last longer. Poor rest can delay improvement. Individual recovery patterns vary widely.2
Why Influenza Can Affect Brain Function
Immune response and inflammation
The flu affects the brain through immune activity. Immune cells release cytokines to control infection. High cytokine levels can influence the blood-brain barrier. This can change how brain cells communicate.3
Temporary changes in brain signaling
Inflammation can impair cognitive function temporarily. The brain may reduce focus on complex tasks. This response helps the body heal. Brain signaling usually normalizes once inflammation settles.
Is Flu Brain Fog Brain Damage?
Flu brain fog is not brain damage. There is no evidence that typical influenza causes permanent injury to the brain in healthy people. Cognitive symptoms are functional, not structural. This distinction helps reduce unnecessary fear.
Many people wonder is brain fog dangerous when cognitive symptoms affect daily tasks, and understanding the underlying cause can help guide appropriate care.
What brain fog is not
Brain fog does not involve neuron loss or structural injury. It does not predict long-term decline. Symptoms reflect temporary changes in signaling. Recovery is expected in most cases.
When neurological evaluation matters
Evaluation is appropriate if symptoms worsen or persist. New neurological signs require attention. Clinicians assess for complications or overlapping conditions.
Managing Flu Brain Fog
What clinicians usually recommend
Management focuses on recovery support. Rest, hydration, and gradual return to daily activities are common recommendations. Pushing through fatigue can prolong symptoms. Recovery is usually gradual.
What recovery depends on
Recovery depends on immune response, sleep quality, and stress levels. Relaxation techniques and steady routines may help. Supportive care allows brain function to normalize over time.⁴
Flu Brain Fog After Vaccination
Why do some people report temporary fog?
Some people report brief mental fog after vaccination. These symptoms reflect immune activation rather than infection. They are usually mild. Most resolve within a few days.
How clinicians interpret these reports
Clinicians view these symptoms as short-term immune effects. The response is smaller than during infection. Current evidence does not suggest long-term cognitive harm.
What People Share Online vs Medical Evidence
Common themes in online discussions
Online forums often highlight severe cases. People share personal experiences and concerns. These stories are real but not typical. Extreme cases receive more attention.
How clinicians assess anecdotal reports
Medical research focuses on population trends. Evidence shows that most flu-related cognitive symptoms resolve. Persistent symptoms warrant clinical review.
When to Seek Medical Care

Medical care is appropriate if symptoms interfere with daily activities or worsen. Severe confusion or new neurological signs require evaluation. Clinicians assess for complications or related conditions.
Dr. Luke Barr, Chief Medical Officer at SensIQ, notes that sleep problems, chronic inflammation, or other viral illnesses can affect recovery. Clinical assessment helps clarify the cause and guide safe next steps.
How Clinicians Evaluate Flu Brain Fog
Clinicians review symptom timing, sleep, and overall health. There is no single test for brain fog. The goal is to identify contributing factors. This approach reflects current medical
Common Questions About Flu Brain Fog
If flu brain fog feels prolonged or raises concern, a healthcare professional can help assess recovery patterns and rule out other causes based on your individual health context..⁵
- Cleveland Clinic. (2024). Brain fog: What it is, causes, symptoms & treatment. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/brain-fog
- National Institutes of Health. (2023). Neuroimmune interactions and cytokine signaling. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Sahyadri Hospital. (2023). Flu brain: Impact of influenza on cognitive health. https://sahyadrihospital.com/blog/flu-brain-a-surprising-impact-of-influenza-on-cognitive-health/
- NeuroHealth Services. (2022). Four ways the flu affects the brain. https://www.neurohealthservices.com/neurohealth-blog/four-ways-the-flu-affects-the-brain/
- Exergen. (2025). Flu brain and neurological effects of influenza. https://www.exergen.com/blog/2025/06/24/flu-brain-the-hidden-neurological-danger-of-influenza-and-why-regular-temperature-monitoring-matters/



