Understanding estrogen vs progesterone helps explain many changes in female bodies. These two hormones work together, but each plays a distinct role in the menstrual cycle, mood, sleep, and energy levels.
Estrogen helps grow and protect tissue, while progesterone helps the corpus luteum prepare the lining of the uterus for a possible pregnancy and maintain more stable hormone levels.
When this balance shifts, people may notice symptoms of menopause, changes in thinking, or new physical discomfort. This guide, co-authored by SensIQ and Dr. Luke Barr, explains what these differences mean and when to consult with your clinician.
SensIQ provides educational resources to help women understand how estrogen and progesterone affect the brain and daily life in perimenopause and menopause.
The goal is not to replace medical care, but to help you ask more informed questions and feel more informed during each visit. Results and experiences vary from person to person. Any treatment choices should always be made in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Key Takeaways
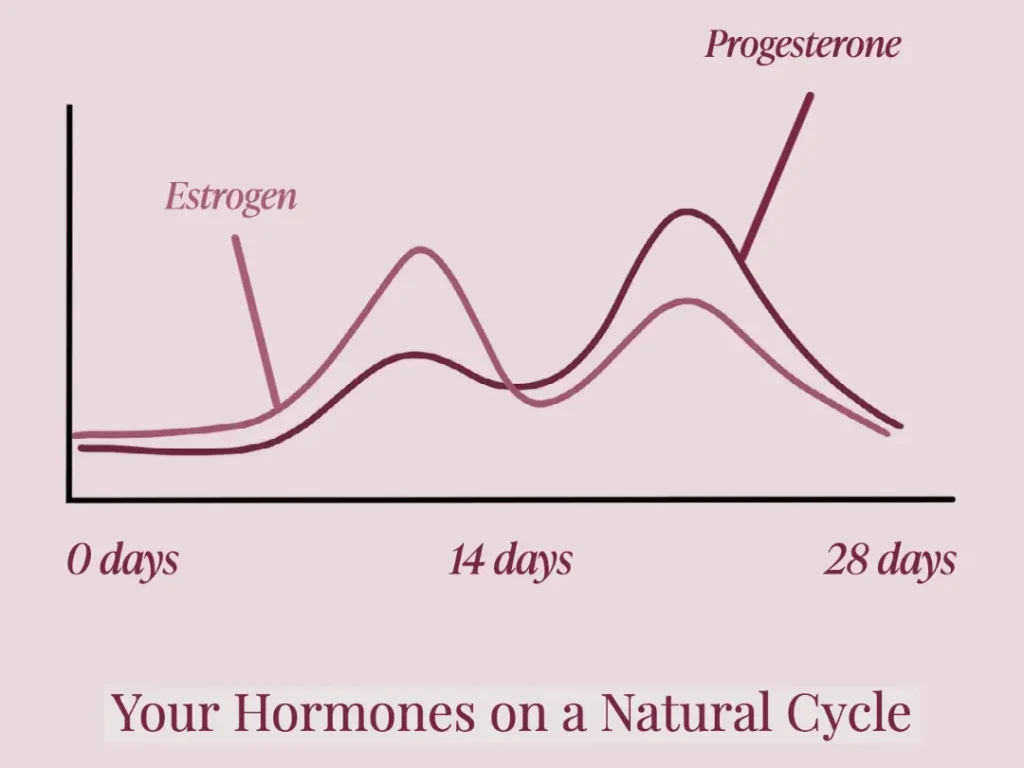
- Estrogen and progesterone regulate key processes in female bodies, and imbalances in their levels can impact mood, sleep, and the menstrual cycle.
- Perimenopause brings unpredictable shifts in hormone levels, which can lead to hot flashes, night sweats, trouble sleeping, and new mood changes.
- Menopause occurs when periods stop and estrogen levels stay low, often leading to symptoms such as brain fog, low energy, or joint discomfort.
- HRT may help ease intense menopausal symptoms under medical supervision, while risks and benefits depend on health history and age.
- Tracking symptoms and working with a clinician can help identify hormone patterns and guide safe decisions about evaluation and support options.
Functions of Progesterone vs Estrogen
Role of Each Hormone
Estrogen is a sex hormone that supports tissue growth, bone strength, and brain function.¹ It helps guide ovulation, shapes the menstrual cycle, and supports the uterine lining.
Progesterone supports early pregnancy and works with estrogen to keep hormone levels in a safer range across the cycle. Both hormones also interact with the adrenal glands, which make small amounts of hormone signals throughout life.
Effects on Energy and Mood
These hormones affect brain areas that regulate focus, calmness, and emotional balance. Steady levels of estrogen often support clear thinking and stable energy.
Progesterone can help the body transition into a state of rest and may support improved sleep quality. When levels of estrogen or progesterone fluctuate rapidly, individuals may experience irritability, fatigue, or increased sensitivity to stress.
Hormonal Changes in Perimenopause and Menopause
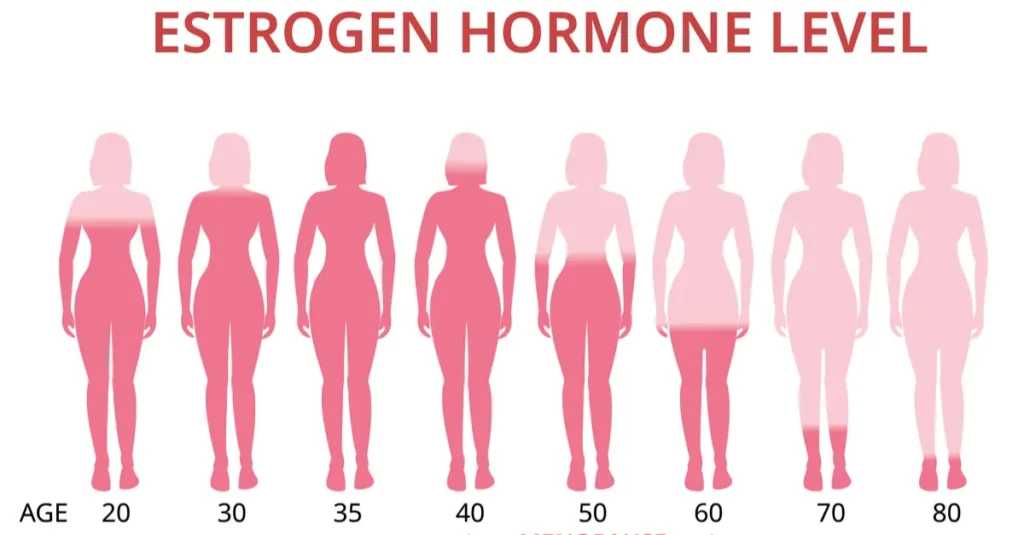
Fluctuations and Declines
Perimenopause brings big ups and downs in hormone levels, and many people describe this phase as unstable or unpredictable.² As estrogen and progesterone fall and rise, you may notice hot flashes in your 30s or 40s, night sweats, trouble sleeping, or mood swings that feel stronger than usual.
Menopause begins when periods stop for 12 months in a row and levels of estrogen stay lower over time. At that point, symptoms of menopause, such as low energy, joint pain, or brain fog, can become more constant and more manageable to notice.
Signs of Low Levels
When estrogen is low, common signs include vaginal dryness, less interest in sex, and small “memory slips,” like losing your train of thought more often. Low progesterone can show up as irregular bleeding, shorter cycles, or feeling more wired, restless, or anxious than usual.
These changes can resemble stress, burnout, or a lack of sleep, so many people blame themselves instead of considering their hormone levels. Keeping a simple record of timing, symptoms, and cycle patterns gives you and your clinician a clearer picture of how estrogen and progesterone may be shifting.
Estrogen vs Progesterone in Hormone Therapy (HRT)
When HRT Is Considered
Hormone replacement therapy HRT may be an option for people with intense menopausal symptoms that affect daily life.³ A clinician may suggest HRT to ease mood swings, hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and other menopausal symptoms after weighing risks and benefits.
This medical treatment differs from non-hormonal products or supplements. It always requires a careful review of age, health history, and family history.
Differences in Treatment
In HRT, estrogen can help reduce many symptoms of menopause that follow a drop in hormone levels. Progesterone is often added when a person still has a uterus, because it helps protect the uterine lining from too much growth.
In some groups, using estrogen alone over time increases the risk of specific problems, including breast cancer, so adding progesterone can lower that risk. Choices around HRT are different from earlier use of birth control pills, and should always be made with clear medical advice.
Comparison Between Estrogen, Progesterone, and Testosterone
Key Differences Between the Hormones
Estrogen supports growth, bone health, and cognitive function, while progesterone brings balance and prepares the uterine lining each cycle. Testosterone is present in female bodies in smaller amounts, supporting muscle mass, energy levels, and sexual drive.
Over time, testosterone levels tend to decline slowly, while those of estrogen and progesterone can drop more sharply. Examining progesterone versus estrogen alone overlooks the broader context of how all three hormones interact with each other.
HRT Side Effects and Risks
Common Side Effects and Important Risks
HRT can cause side effects such as breast tenderness, mild bloating, or mood shifts. Some people also notice headaches or light nausea when treatment starts or doses change.
Studies suggest that some estrogen-based therapies are tied to an increased risk of blood clots or breast cancer in certain groups, especially when therapy continues for many years.⁴ A clinician reviews where treatment increases the risk and where it may still be reasonable based on symptoms and overall health.
Evaluation and Clinical Support
When to Consult a Professional
It is essential to see a clinician if bleeding changes a lot, sleep problems feel severe, or mood changes make work and home life difficult. Sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, or one swollen leg can be warning signs for blood clots and need fast care.
Your clinician may order tests to check levels of estrogen and progesterone, as well as other hormone levels, to rule out thyroid or other hormonal problems. SensIQ offers non-hormonal educational support that may help improve mental clarity and reduce stress, allowing you and your clinician to determine the best plan together.*
References
- Healthline. (n.d.). Estrogen vs. progesterone: Functions in the human body. In Healthline. Retrieved November 14, 2025, from https://www.healthline.com/health/womens-health/estrogen-vs-progesterone
- Nebraska Medicine. (2025, May 30). What is the difference between estrogen and progesterone? In Nebraska Medicine Health. Retrieved November 14, 2025, from https://www.nebraskamed.com/health/conditions-and-services/womens-health/what-is-the-difference-between-estrogen-and
- Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Hormone therapy for menopause symptoms. In the Cleveland Clinic. Retrieved November 14, 2025, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/15245-hormone-therapy-for-menopause-symptoms
- MedlinePlus. (2024, September 9). Hormone replacement therapy. In MedlinePlus. Retrieved November 14, 2025, from https://medlineplus.gov/hormonereplacementtherapy.html
*These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.